Why Choose a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) Over a Relay-Based System?
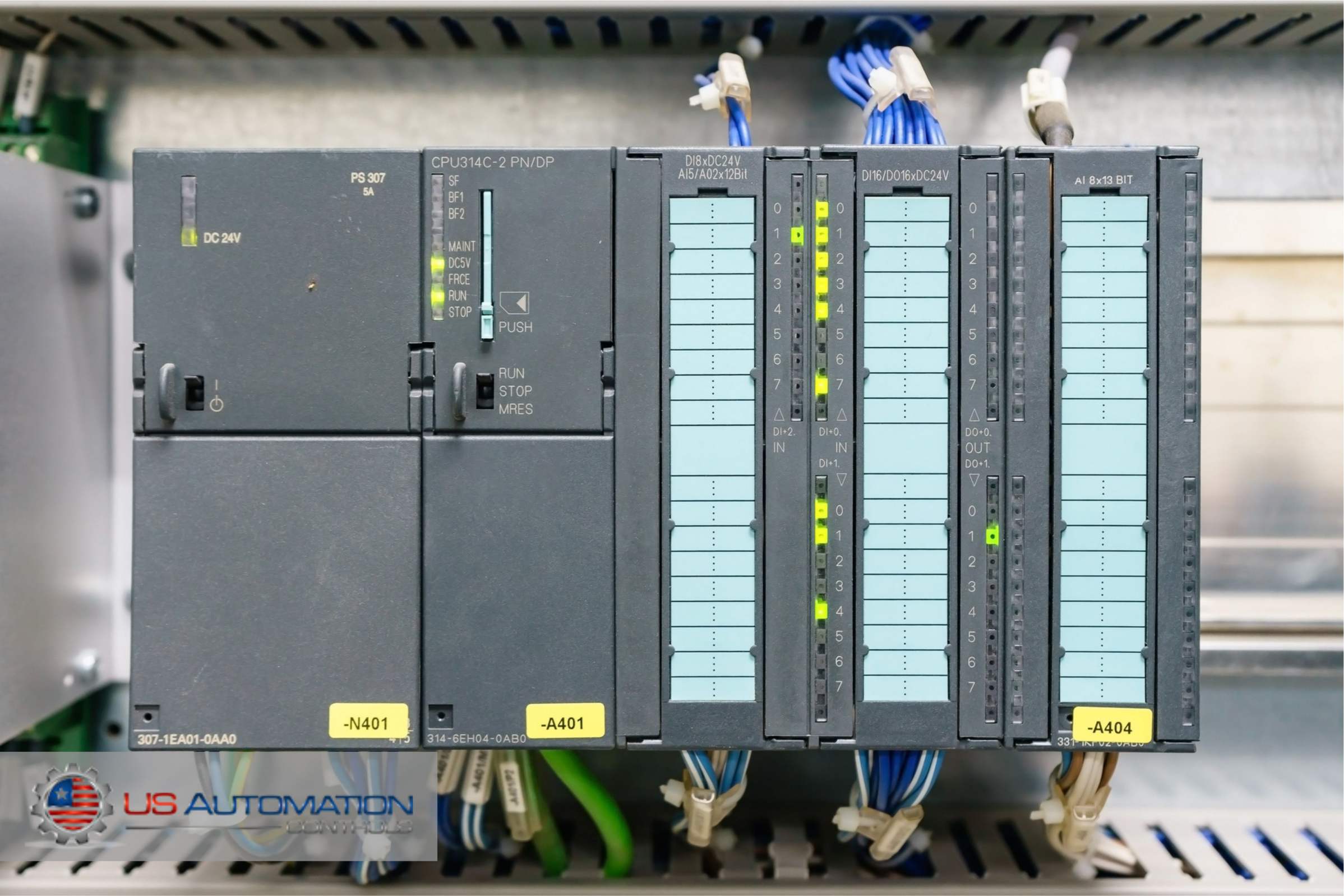

When you want to choose the best tools and devices for industrial wiring, learning the differences between PLCs and relay-based systems is imperative. Since PLCs and relay logic are both used for industrial automation, choosing the proper control system is crucial to performance and safety in an automated industrial setting. Moreover, other important factors like flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness also depend heavily on whether you choose PLCs or relay-based systems.
In this article, you will read about the differences between PLCs and relay logic, the advantages of PLCs over relay logic, and the use cases where it's wiser to choose a programmable logic controller over a relay-based system.
Know the Difference
Let's dive into the differences between Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and relays. We will discuss the differences between the two from five perspectives:
Control Method
As the key difference between the two control systems, their control methods make much difference when you're working with them. Relays use an electromechanical control method, while PLCs use digital programming to control operations.
How does that affect the process of using the two control systems? Read along to find out!
Flexibility
Since relay-based systems use mechanical wiring to control operations, they are hardwired, and changing their functionality requires manual modification of the circuits.
On the other hand, PLCs are not only programmable, but also reprogrammable. That's why making changes to the functionality of a PLC system does not require re-wiring any parts of the control system.


Integration
PLCs can be integrated with several other parts of the digital automation control systems. Some examples of what PLCs can easily communicate with are SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) and HMIs (Human-Machine Interfaces). In contrast, relays offer minimal integration. Integrating a relay-based system with other systems, if possible, should take place manually.
Complexity and Cost
Since PLCs are digital components that control the automation system based on computer code, using them includes writing computer code and requires programming skills. Conversely, using relays requires manually setting up circuits and does not require programming. Moreover, PLCs cost more than relays.
Maintenance
Overall, maintaining optimal conditions in PLCs and relays are almost entirely different processes. In brief, PLCs require electronic and software maintenance like firmware updates, and relays require mechanical maintenance and fewer updates.
Why Choose PLC Over Relay?
Next, let's explore the several ways in which PLCs' differences with relay-based systems are advantageous:
Flexibility
PLCs are far more flexible than relay-based systems. As mentioned above, PLCs are programmable, which means you can program the same physical device to have different functionalities, and if more is needed, one PLC can control many operations. Not only do relays depend on manual modification to determine their functionality, but they are also hardwired and should be manually modified if you want to make changes to their functionality.
All of the factors mentioned above make PLCs much more flexible, and more easily programmable for different tasks without making changes to the hardware.
Integration With Other Common Systems
Whether you are using a PLC-based or a relay-based control system, its integration with other systems is an essential part of the automation problem. For more seamless automation control, it is imperative that your control system is integrated well with other systems. This integration happens with little to no trouble when you use PLCs. As mentioned above, there are many other helpful automation systems, such as SCADA and HMIs, with which PLCs can easily be integrated.
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Since PLCs are electronic devices that work with computer programs, they also include advanced diagnostic software that can quickly identify issues. This automatic detection of issues makes troubleshooting far easier and reduces downtime.
Centralized Control
With relays, you have each part of your control system in one corner, doing its job. If you want to make sure every relay is working correctly, you will have to take a tour, or at least check many different components in one location.
On the other hand, PLCs control multiple devices from one central location. This makes checking and even reprogramming all operations possible from a single location.

Reliability
Since PLCs are less susceptible to mechanical failure and include self-diagnostic software, they are more reliable than relays–which are prone to mechanical failure and need manual troubleshooting.
Safety and Maintenance
Safety and maintenance are also areas where PLCs are preferable. PLCs have built-in safety features like emergency stop buttons and interlocks that protect operators and equipment. Additionally, PLC systems require less maintenance over time since, unlike relays, they don't suffer from mechanical wear. That's why the reduced maintenance and downtime can make PLCs more cost-effective in the long run despite their initial cost.
Use Cases of PLCs in Industrial Wiring
Some examples of PLCs' many usages in industrial settings are:
- One prominent use case is in manufacturing automation. Here, PLCs control entire production lines and ensure faster production times and higher product consistency by automating tasks such as assembly, sorting, and quality control.
- In the food and beverage industry, PLCs play a crucial role in automating packaging and quality checks since they can be easily reprogrammed to handle different product lines.
- In energy management, PLCs help optimize the use of resources by monitoring and adjusting systems to ensure efficient energy consumption.
Buy High-Quality PLCs from Your Trusted Automation Controls Supplier in Short Hills, NJ
Do you need PLCs for your US automation control system? Buy from USAC! As premier distributors and suppliers with more than 50 years of experience, we know our customers' every need and tend to them.
If you need first-grade PLCs and their components, don't wait! Contact us now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between a PLC and a relay system?
A PLC is a digital control system that uses programming to automate tasks, while a relay system uses electromechanical switches to control circuits.
Can I replace a relay system with a PLC?
Yes, in most cases, a PLC can replace a relay system, especially if you need more flexibility, advanced diagnostics, and centralized control.
Are PLCs challenging to program?
Programming a PLC can be challenging for beginners, but many user-friendly programming languages and interfaces simplify the process.
Are PLCs suitable for small-scale applications?
For small-scale applications with simple tasks and a limited budget, a relay system might be more cost-effective. PLCs are better suited for more complex and scalable operations.
How do PLCs improve system safety?
PLCs have built-in safety features like emergency stops and interlocks, which help protect equipment and operators in industrial environments.







